By the editorial staff of Allodocteurs.fr
Written on
, Updated
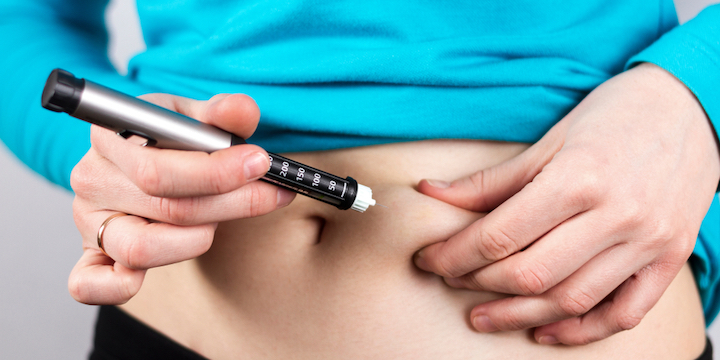
This is the lot of many diabetics: injecting insulin daily to regulate their blood sugar. But be careful not to always perform these injections in the same area of the body, warns the independent medical journal Prescribe.
“In the event of long-repeated insulin injections in the same area, tissue changes appear, disrupting its distribution, resulting in poor glycemic control and an increase in the frequency of hypoglycaemia“she writes in her August 2021 issue.
Read also: Insulin pump: the freedom to eat everything?
Nodules under the skin
Of course, repeated injections over a long period in the same area are less painful than by regularly changing areas. But the subcutaneous adipose tissue, that is, the fat located just under the skin, changes below the injection site.
More precisely, nodules or thickenings called lipohypertrophies form there. And the problem is that these thickenings vary “irregular and unpredictable“insulin absorption. This leads to poor glycemic control and therefore an increase in the frequency of hypoglycaemia.
Years for a recovery
The ideal is therefore to respect the rotations of the injection zones. While knowing that after stopping injections in a given area, the regression of lipohypertrophies is slow: it takes a few months, or even years.
When should I change zones?
But how do you spot the first signs? “The absence of pain on injection is an indicator of tissue remodeling“explains Prescrire.
It is also the role of caregivers of “identify these areas by visual examination and palpation “, and help the patient to organize a system of zone rotations.
 Cherry tomatoes contaminated with salmonella: 92 sick and 1 dead
Cherry tomatoes contaminated with salmonella: 92 sick and 1 dead  A better coaching method can make a person grow
A better coaching method can make a person grow  What is the method to prevent diabetes in children?
What is the method to prevent diabetes in children?  What are the effective factors in causing stomach ulcers?
What are the effective factors in causing stomach ulcers?  Why do embarrassing memories seem to appear at night?
Why do embarrassing memories seem to appear at night?  The amazing link between SARS-CoV-2 infection and newly started diabetes
The amazing link between SARS-CoV-2 infection and newly started diabetes  WHO says monkey pox is not a global emergency right now
WHO says monkey pox is not a global emergency right now  Single cell RNA sequencing uncovers new mechanisms of heart disease
Single cell RNA sequencing uncovers new mechanisms of heart disease  Hepatitis of unknown origin: 3 new deaths and 228 cases worldwide
Hepatitis of unknown origin: 3 new deaths and 228 cases worldwide